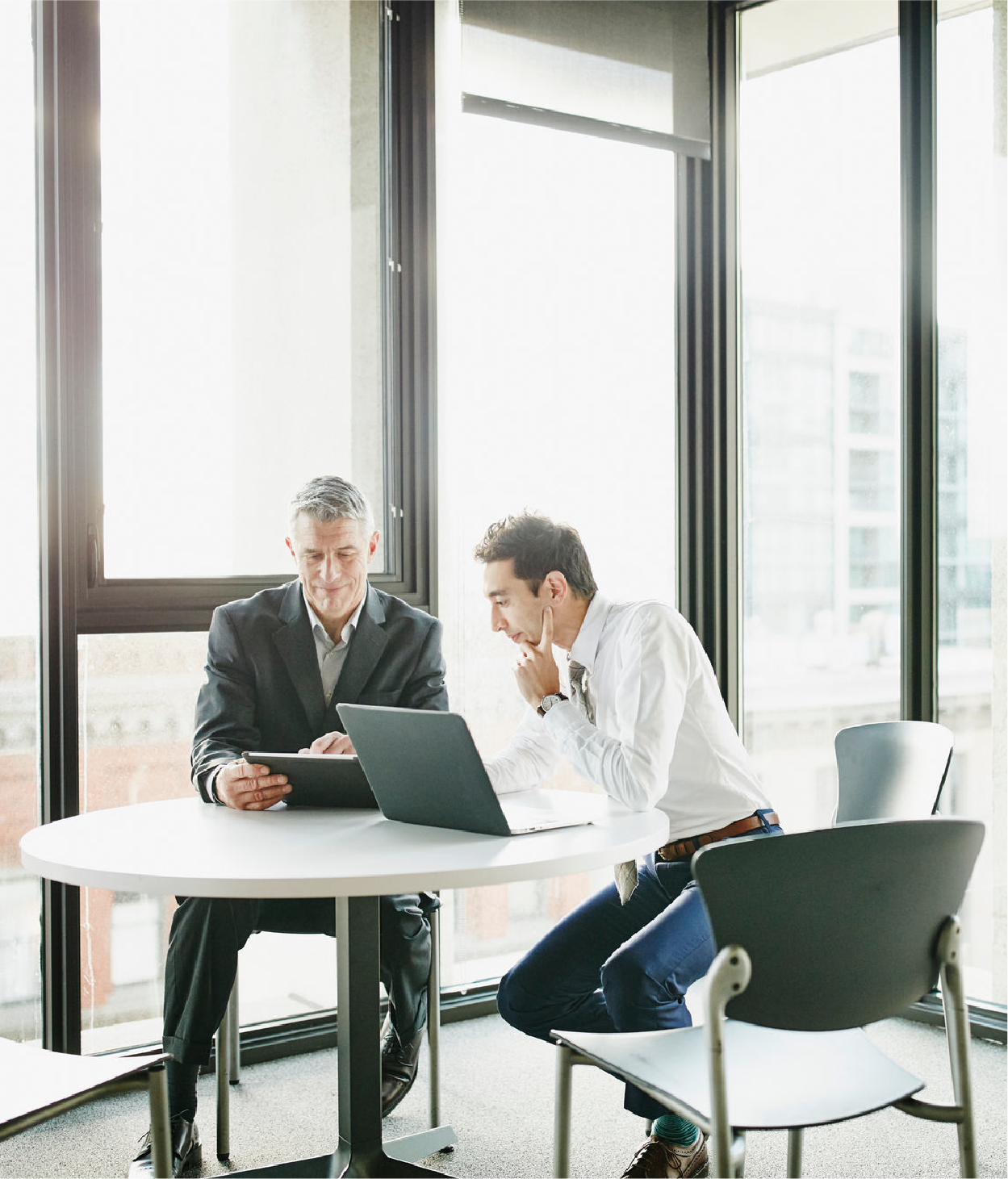
With this much available information, it’s no wonder 95% of businesses say they need to improve the data governance processes associated with their unstructured data.
This data explosion trend creates both opportunities and challenges for controlling an organization’s data, particularly regarding data retention policies.
Data retention opportunities
The exchange of personal data provides a gateway for businesses to offer value to their customers and build trust with them, as long as the business respects the customer’s consent and preferences. An example here is that about 7 in 10 consumers are willing to share health, exercise, and driving habit data to access lower insurance rates. This represents a 19% increase in two years. But the caveat here is that customers only share this data if they believe it will be retained, used, and protected appropriately.
Equipped with more data sets, teams can improve how they innovate, accelerate change, and provide personalized consumer experiences. By balancing business requirements while mitigating risk with this data-value exchange, organizations stand to gain better customer loyalty outcomes, increased profitability, and decreased risk of non-compliance.
Data retention challenges
While many organizations develop retention policies, they require a significant effort to implement. That’s why among 80% of companies with a defined data retention policy, only one in three actively tag data with its destruction date and information. Additionally, anonymization and pseudonymization, two ways of helping protect privacy and eliminating the need to destroy or delete data, aren’t widespread, with only 17% of organizations adopting these practices.
When businesses don’t practice sound data governance, consumer trust erodes. About 50% of internet users are more likely to trust a company that limits the amount of personal information they collect about data subjects. However, this approach isn’t always an option depending on the industry.
Put data retention policies into practice
By automating data retention, organizations can take another step towards securing consumer trust. While most data privacy teams, business process owners, and other stakeholders can agree on this, the inherent challenge is consistently scaling the effort across various (and often inconsistent) data types and locations.
Traditionally, operationalizing an effective data retention policy is labor-intensive. In many workplaces, locating different data in violation of policy is a manual process that requires combing through customer data manually.
This isn’t a realistic approach, given the volume and types of data that businesses process on a day-to-day basis. There’s an urgent need to develop processes that responsibly handle data throughout its lifecycle at scale. These processes should be able to answer — and sustainably operationalize — these four questions:
- How long should I retain this data?
- In what cases should I hold onto data beyond its retention period without creating additional security issues?
- In what circumstances should I immediately erase data once outside its retention period?
- What amount of time should my team hold onto data without established retention periods?
Manual processes no longer need to represent the status quo for record retention. Today’s privacy teams can leverage automation to operationalize data retention policies to meet regulatory requirements and business needs at scale.
By analyzing and flagging retention violations through automation, teams can enforce data retention schedules and minimization policies faster and more effectively. This is especially helpful when you can centralize these processes in a single system to streamline regulatory compliance efforts and de-risk the digital information your company controls.
Benefits of an automated data retention and deletion program
Teams that work with automated data retention and deletion programs can expect to:
- Reduce attack surfaces: the more data an organization stores, the larger the target they are for attackers looking to steal that data. Reducing the volume of data will also decrease the potential for data loss and an organization’s liability for damages.
- Improve security practices: Understanding the data you have and must protect is key to any security program. And the more context you have about the data, including how long it should be kept (or when it can be deleted), helps to ensure that security teams are investing their time and resources to protect only relevant, necessary data.
- Streamline data costs: Data storage is costly. Between security efforts, audits, and privacy operations, the storage costs associated with data aren’t insignificant. Secure data erasure as part of an automated data retention program allows businesses to reuse storage media in a compliant and cost-effective manner. This is especially true compared to the costs of destroying and replacing storage media.
Gain visibility and take action to de-risk your organization’s staggering amount of data. Learn how to implement those strategies in this infographic.