A horizontal approach: Standing apart on the global stage
In crafting its approach to artificial intelligence (AI) legislation, the European Union (EU) has opted for a horizontal legislative framework. The EU’s AI legal framework embraces an industry-agnostic perspective and is meticulously designed with nearly a hundred articles.
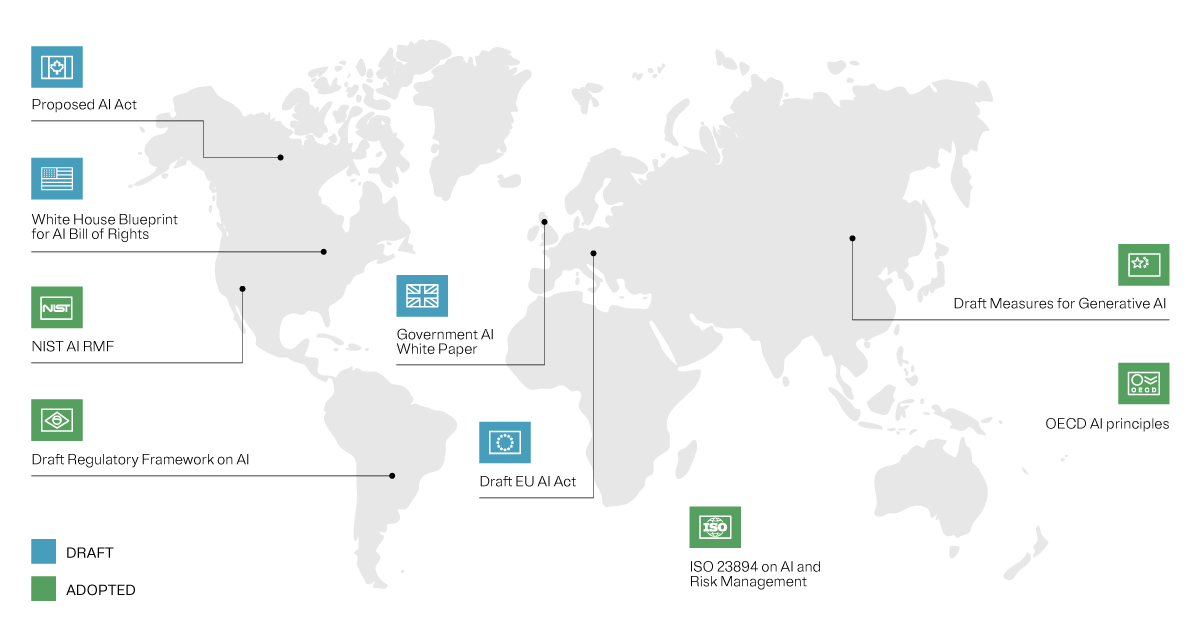
Here, we’ll look to provide a window into the EU AI Act. This piece of legislation is not just the first of its kind—but also a benchmark for global AI regulation, developed to help create a precedent in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
Guarding values, fueling innovation
The EU AI Act is carefully balanced. It’s not just about throwing a safety net around society, economy, fundamental rights, and the bedrock values of Europe that might be at risk due to AI systems; it’s also a nod to the power and potential of AI innovation, with built-in safeguards designed to promote and protect inventive AI strides. It looks to strike the balance of risk management and protecting critical infrastructure from potential pitfalls, while promoting the innovations that general-purpose AI can bring with it.
Crafting the EU AI Act has been anything but a walk in the park, with the definition of AI being one of the contentious corners. Since its inception proposal in April 2021, the Act has been a living document, seeing numerous iterations, each amendment reflecting the fluid discourse around AI technology and its implications for society.
At the trilogue meeting in December, France, Germany, and Italy raised concerns about the limitations placed on powerful AI models, and wanted to take a lighter regulatory regime for models like OpenAI’s GPT-4.
After ongoing discussion, the compromise reached by the EU commission was to take a tiered approach, with horizontal transparency rules for all models and additional obligations for compelling models with systemic risk.
Where the Act stands now
On February 2, 2024, the Committee of Permanent Representatives voted to endorse the political agreement reached in December of 2023. On March 13, Parliament voted to endorse the Act, with 523 votes in favor, 46 against and 49 abstentions.
The AI Act will enter into force 20 days after its publication in the EU’s Office Journal. The provisions on prohibited systems will apply after 6 months, and obligations for providers of general-purpose AI will apply after 12 months. Most other requirements will apply after two years.
High risk systems that are intended to be used as a safety component of a product or are covered by other laws in the EU have 36 months to comply with the EU AI Act.
AI: Breaking down the concept
Originally, the Act defined machine learning, the basis of AI systems, as “including supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning, using a wide variety of methods including deep learning.” The text includes an updated definition, which defines AI systems as “machine-based systems designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy and that may exhibit adaptiveness after deployment and that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or virtual environments.”
The complexity of AI systems is a sliding scale, with more intricate systems requiring substantial computing power and input data. The output from these systems can be simple or mightily complex, varying with the sophistication of the AI in play.
This broad definition covers a range of technologies, from your everyday chatbots to highly sophisticated generative AI models. But it’s important to note that not every AI system falling under the Act’s broad definition will be regulated. The Act plays it smart with a risk-based approach, bringing under its regulatory umbrella only those systems associated with specific risk levels.AI regulation: Calibrated to risk
AI Regulation: Calibrated to Risk
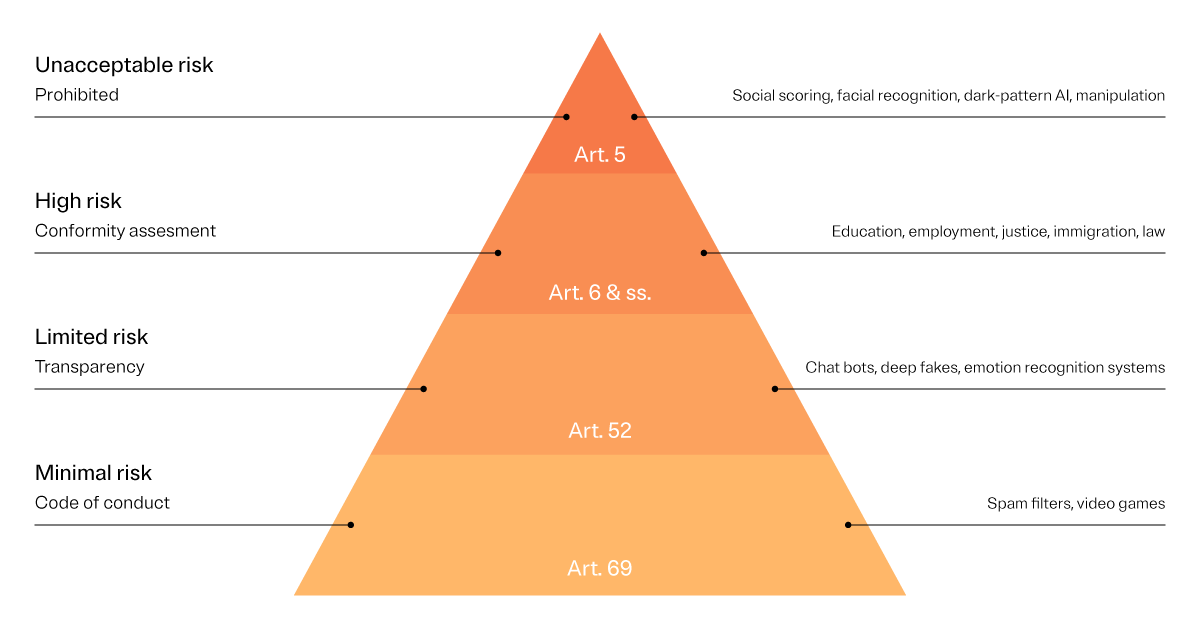
Here’s where it gets interesting. The EU AI Act has different baskets for AI systems. Some are seen as posing an unacceptable risk to European values, leading to their prohibition. High-risk systems, while not banned, have to dance to a tighter regulatory tune. It’s vital to remember that these risk categories aren't static; the Act is still in a draft stage, and as more changes come, these risk categories will likely be fine-tuned as well.
EU AI Act risk levels
The EU AI Act defines multiple levels of permissible risk: high risk, limited risk, and minimal risk.
These are the levels of “permissible risk” that are allowed by organizations, however, “unacceptable risk” is a risk level which is not allowed by organizations at which point companies need to change their models accordingly.